Tutorial¶
Learning guide for basic usage of rcontrol.
Executing a command on a remote host¶
To execute a command, you first need to create a session. A session is usually used inside a with block, to ensure that all tasks will finish and that the connection will be closed at the end.
from rcontrol.ssh import ssh_client, SshSession
# create a ssh connection. This basically create a connected
# paramiko.SSHClient instance.
conn = ssh_client('localhost', 'jp', 'jp')
# execute the command
with SshSession(conn) as session:
session.execute("uname -a")
# outside the with statement, all tasks are done and the connection
# is automatically closed.
If you ran this snippet, you will see nothing on the screen. This is because there is no handler defined for the command output:
from rcontrol.ssh import ssh_client, SshSession
def on_finished(task):
print("finished (exit code: %d) !" % task.exit_code())
def on_output(task, line):
print("output: %s" % line)
conn = ssh_client('localhost', 'jp', 'jp')
with SshSession(conn) as session:
session.execute("uname -a", on_stdout=on_output, on_finished=on_finished)
Output:
output: Linux JP-Precision-T1500 3.13.0-39-generic #66-Ubuntu SMP Tue Oct 28 13:30:27 UTC 2014 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux
finished (exit code: 0) !
Synchronizing commands¶
Here is an example of how to synchronize tasks. To run two commands in parallel, then wait for them to finish an run a last command after that:
from rcontrol.ssh import ssh_client, SshSession
conn = ssh_client('localhost', 'jp', 'jp')
with SshSession(conn) as session:
# this will run in parallel
task1 = session.execute("sleep 1; touch /tmp/rcontrol1.test")
task2 = session.execute("sleep 1; touch /tmp/rcontrol2.test")
# now wait for the commands to complete
task1.wait()
task2.wait()
# or session.wait_for_tasks()
# and do something else
session.execute("rm /tmp/rcontrol{1,2}.test")
# no need to wait for this task, it will be done automatically
# since we are in the with block
See also
Executing local commands¶
Local commands can be executed in the same way as remote ones. Just use
a rcontrol.local.LocalSession:
from rcontrol.local import LocalSession
with LocalSession() as session:
session.execute("touch /tmp/stuff")
Executing commands on multiple hosts¶
It is recommended to use a session manager to work with multiple hosts at the same time:
from rcontrol.ssh import SshSession, ssh_client
from rcontrol.core import SessionManager
with SessionManager() as sessions:
# create sessions
sessions.bilbo = SshSession(
ssh_client('http://bilbo.domain.com', 'user', 'pwd'))
sessions.nazgul = SshSession(
ssh_client('http://nazgul.domain.com', 'user', 'pwd'))
# run commands in parallel
sessions.bilbo.execute("someLongCommand")
sessions.nazgul.execute("anotherCommand")
# wait for these commands to finish, then run a last one
sessions.wait_for_tasks()
sessions.nazgul.execute("echo 'Done !'")
More on commands synchronisation¶
Let’s say we have to execute some commands on multiple hosts:
T1, T2, T3 will be started at the same time. Once T1 is finished, T11 and T12 tasks must be started. Once T11, T12 and T2 are finished, T4 must be started. Finally, we can start T5 once T4 and T3 are finished.
T1, T11, T12, T5 must be executed on atlas2.
T2, T4 must be executed on bilbo.
T3 must be executed on nazgul.
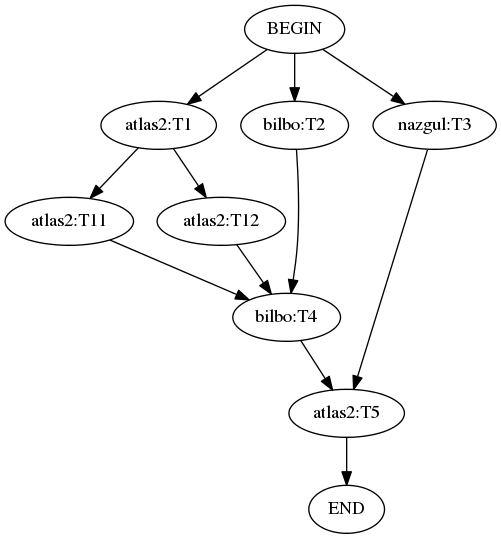
Here is a possible implementation:
from rcontrol.ssh import SshSession, ssh_client
from rcontrol.core import SessionManager
def show(task, line):
LOG.info('%s: %s', task.session, line)
with SessionManager() as sessions:
# create sessions
sessions.atlas2 = SshSession(
ssh_client('http://atlas2.domain.com', 'user', 'pwd'))
sessions.bilbo = SshSession(
ssh_client('http://bilbo.domain.com', 'user', 'pwd'))
sessions.nazgul = SshSession(
ssh_client('http://nazgul.domain.com', 'user', 'pwd'))
def sub_build(task):
task.session.execute("echo 'task 11'", on_stdout=show)
task.session.execute("echo 'task 12'", on_stdout=show)
sessions.atlas2.execute("echo 'task 1'", on_finished=sub_build, on_stdout=show)
sessions.bilbo.execute("echo 'task 2'", on_stdout=show)
sessions.nazgul.execute("echo 'task 3'", on_stdout=show)
# wait for tasks on atlas2 and bilbo
# note that the build 3 task on nazgul still run in the background
sessions.atlas2.wait_for_tasks()
sessions.bilbo.wait_for_tasks()
# now run another build
sessions.bilbo.execute("echo 'task 4'", on_stdout=show)
# wait for task 3 and 4 (all active tasks)
sessions.wait_for_tasks()
# and finally run a last task
sessions.atlas2.execute("echo 'task 5'", on_stdout=show)
Note
In this example, errors are not handled. If an error occurs during a task execution, following tasks won’t be executed and the error(s) will be raised as soon as possible.
Copy files and directories between hosts¶
Here is an example that show how to copy files and directories accros computer.
Note that you can use the rcontrol.local.LocalSession to get or put
files and directories locally.
from rcontrol.ssh import SshSession, ssh_client
from rcontrol.core import SessionManager
with SessionManager() as sessions:
# create sessions
sessions.bilbo = SshSession(
ssh_client('http://bilbo.domain.com', 'user', 'pwd'))
sessions.nazgul = SshSession(
ssh_client('http://nazgul.domain.com', 'user', 'pwd'))
# copy a file on nazgul, block until it is done
sessions.bilbo.s_copy_file('/tmp/stuff', sessions.nazgul, '/tmp/stuff')
# copy recursive dirs in a non blocking way (you can synchronize it just
# like commands)
# Note that the destination folder /tmp/dir on nazgul must not exists
sessions.bilbo.copy_dir('/home/my/dir', sessions.nazgul, '/tmp/dir')
See also